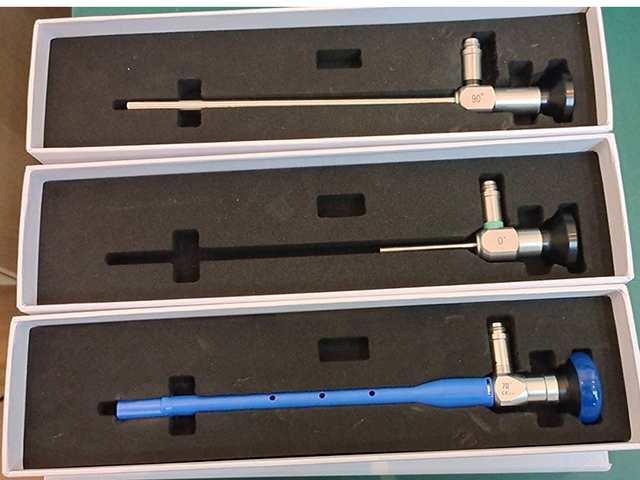
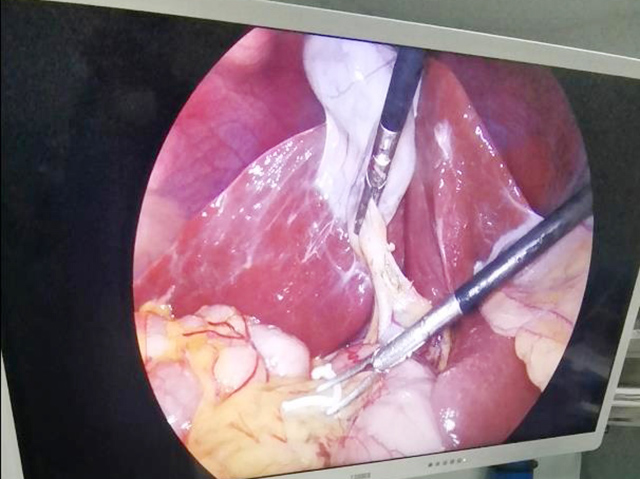
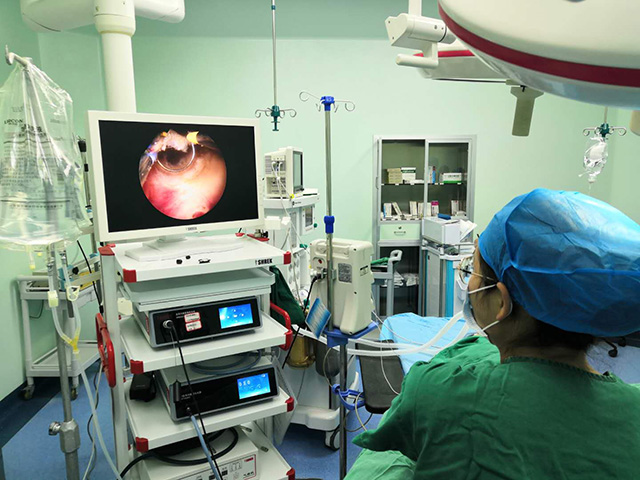
An ear nose throat endoscope, also known as an ENT endoscope, is a medical device that is used to examine the internal structures of the ear, nose, and throat. It consists of a long, thin, flexible tube with a camera and light at the end, which is inserted through the patient's nostril, mouth, or ear canal to provide a clear view of the internal structures.
There are two main types of ENT endoscopes:
Rigid endoscopes: These are straight, inflexible tubes with a fixed angle and are commonly used for nasal and sinus surgery. They provide a high-quality, high-resolution image but can be uncomfortable for the patient.
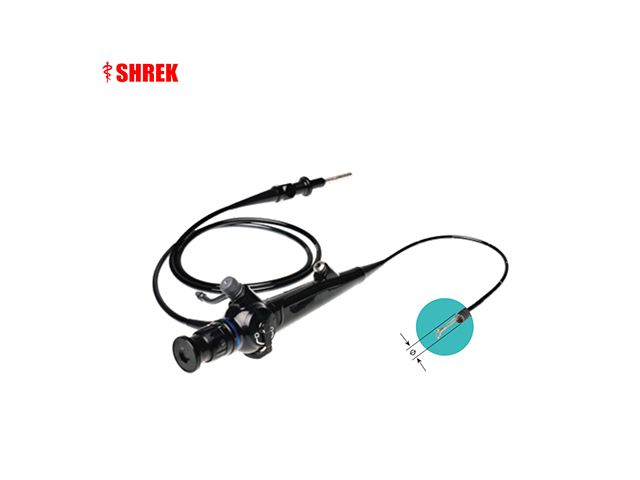
Flexible endoscopes: These are long, thin, flexible tubes with a camera and light at the end, which can be inserted through the patient's nostril, mouth, or ear canal. They are more comfortable for the patient and can be used for a wider range of procedures, such as examining the vocal cords or the middle ear.
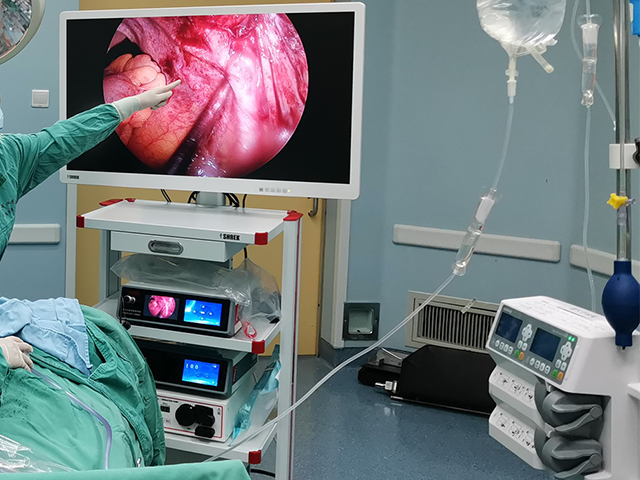
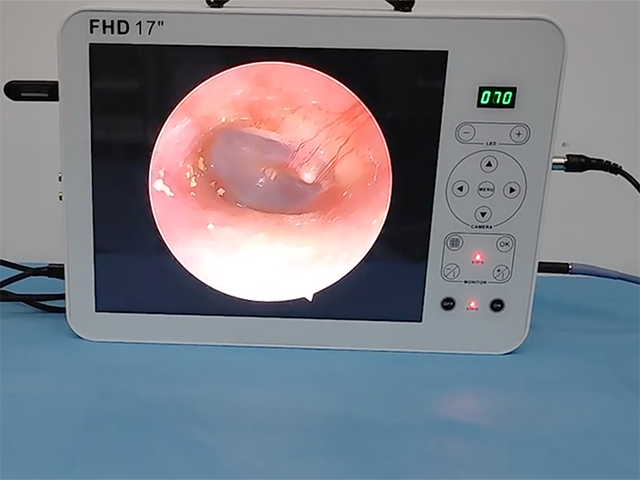
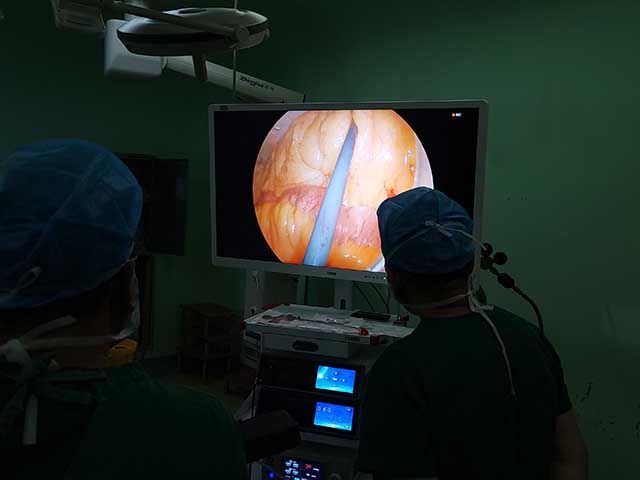
ENT endoscopes are commonly used by otolaryngologists, or ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists, to diagnose and treat a variety of conditions, such as sinusitis, nasal polyps, tonsillitis, ear infections, and vocal cord disorders. The images captured by the endoscope can also be recorded and used for further analysis or shared with other medical professionals.
When choosing medical endoscopic cameras for otolaryngology, there are several factors to consider:
Image quality: The image quality is the most critical factor in choosing an endoscopic camera. The camera should provide high-definition images with good color reproduction, sharpness, and contrast to help the surgeon see the details of the internal structures clearly.
Compatibility: The endoscopic camera should be compatible with the endoscope being used. The camera should be able to connect easily to the endoscope, and the images should be easily transferable to the monitor.
Size and weight: The size and weight of the camera should be lightweight and compact, making it easy for the surgeon to handle and maneuver during the procedure.
Durability and reliability: The endoscopic camera should be durable and reliable, able to withstand the rigors of daily use and able to function consistently without interruption.
Ergonomics: The endoscopic camera should be ergonomically designed to reduce fatigue and strain on the surgeon's hands and wrist during the procedure.
Cost: The cost of the endoscopic camera is also an essential factor to consider. The camera should be cost-effective, providing good value for money without compromising on quality.
Support and service: The manufacturer of the endoscopic camera should provide excellent customer support and service to ensure any technical issues can be resolved quickly and efficiently.
In summary, when choosing medical endoscopic cameras for otolaryngology, it's essential to consider image quality, compatibility, size and weight, durability and reliability, ergonomics, cost, and support and service.






Leave A Inquiry