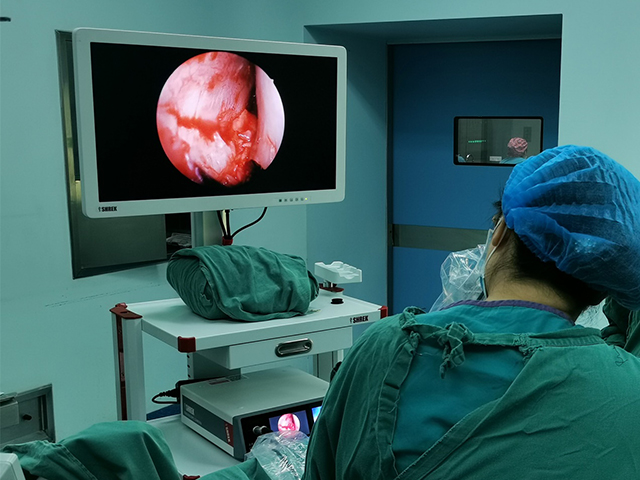
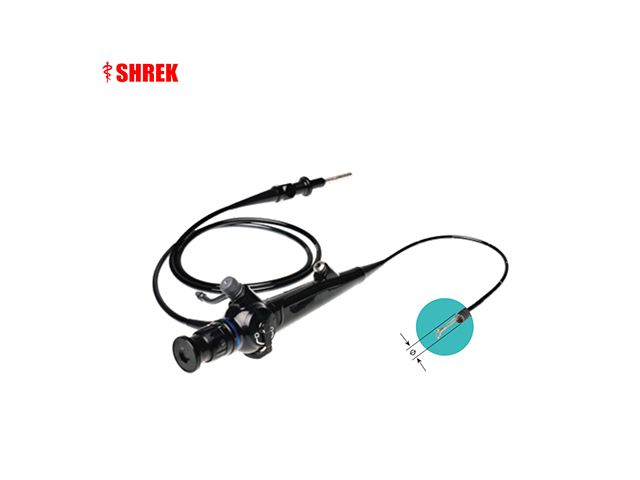
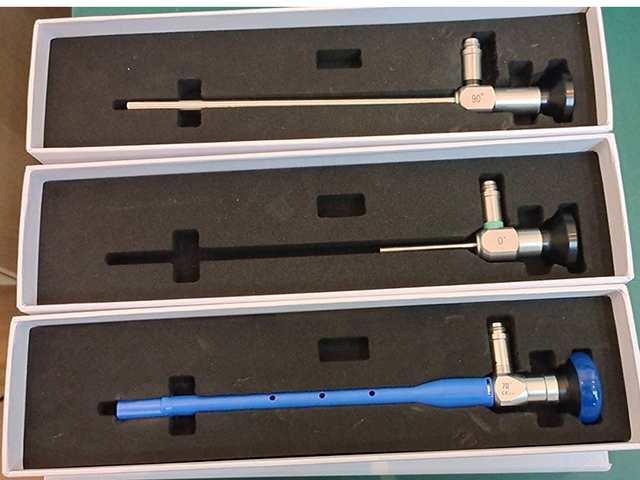
An ear nose throat (ENT) endoscope is a medical device that is designed to examine the ear, nose, and throat. When examining the throat, the endoscope is inserted through the mouth and down the throat. Here's how it typically works:
Preparation: Before the endoscope is inserted, the patient will be asked to open their mouth wide and may be given a numbing spray or gargle to help reduce discomfort.
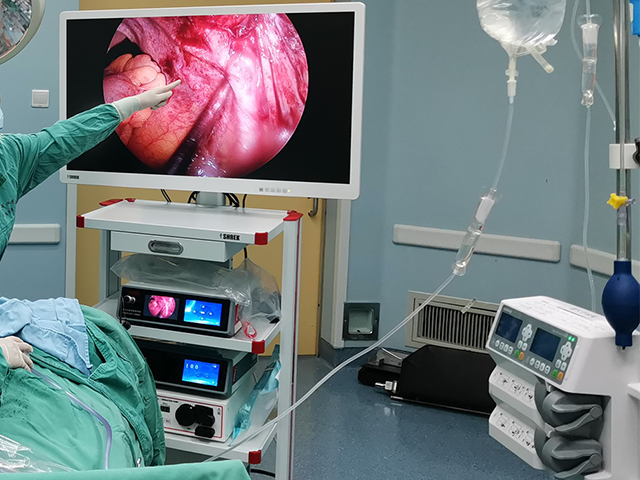
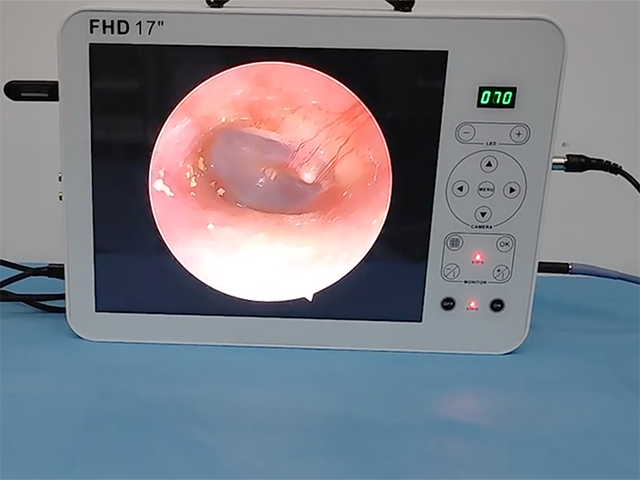
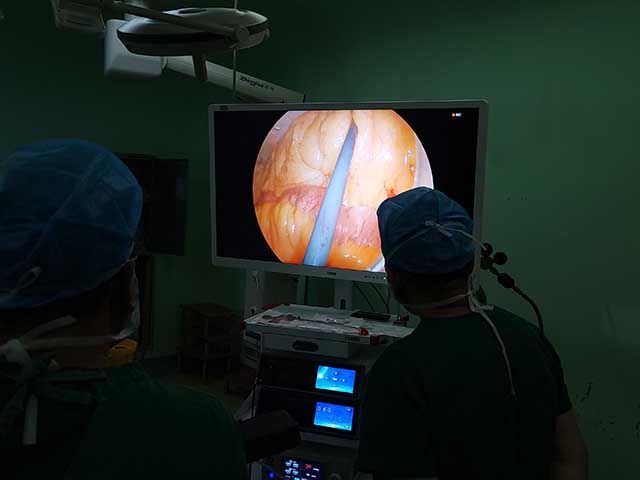
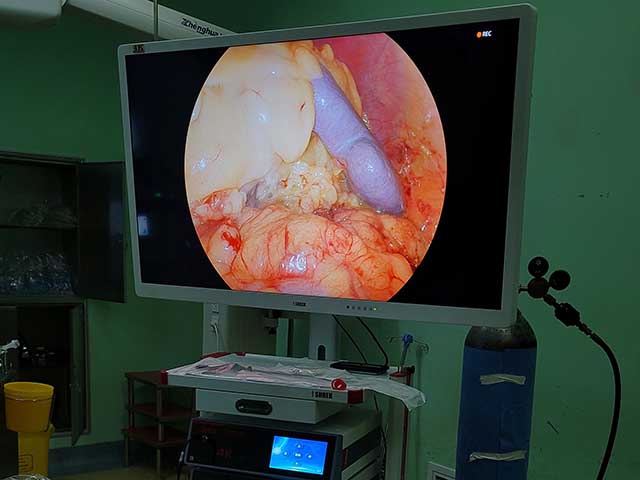
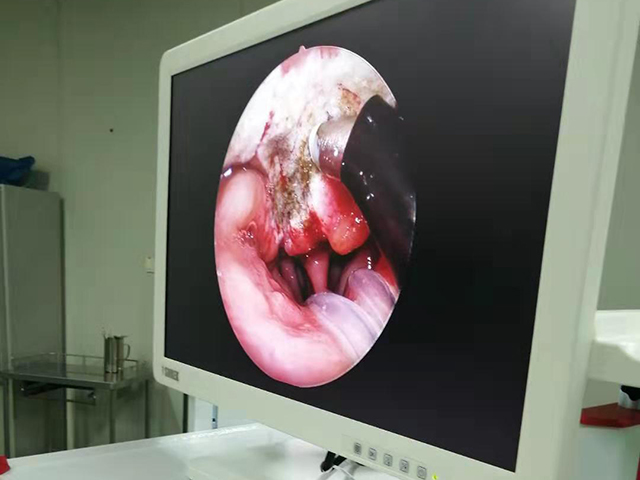
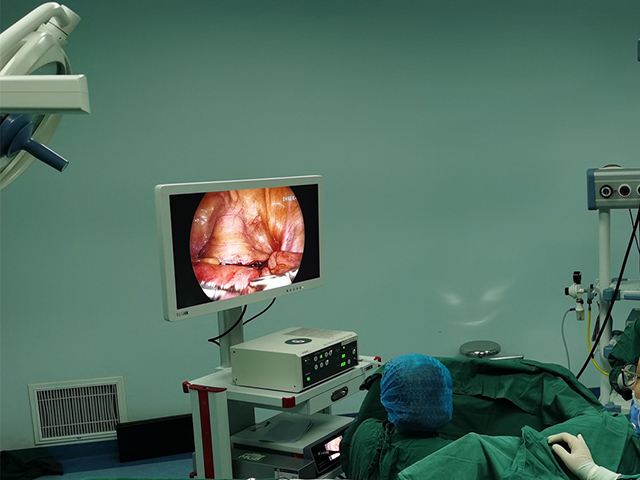
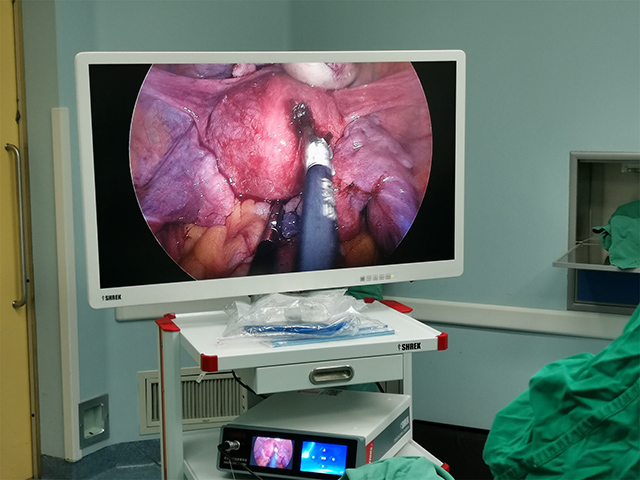
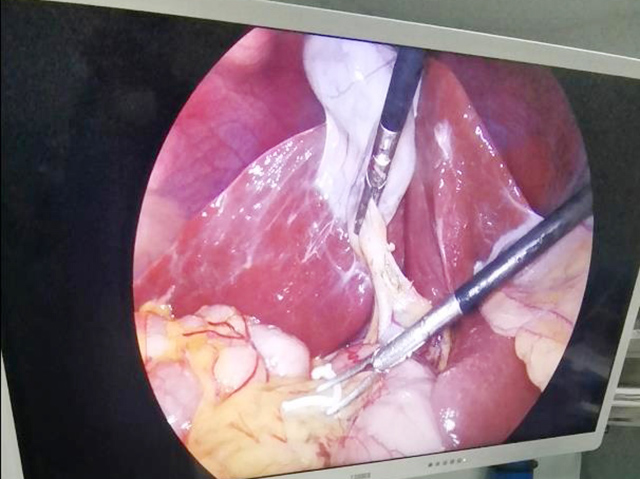
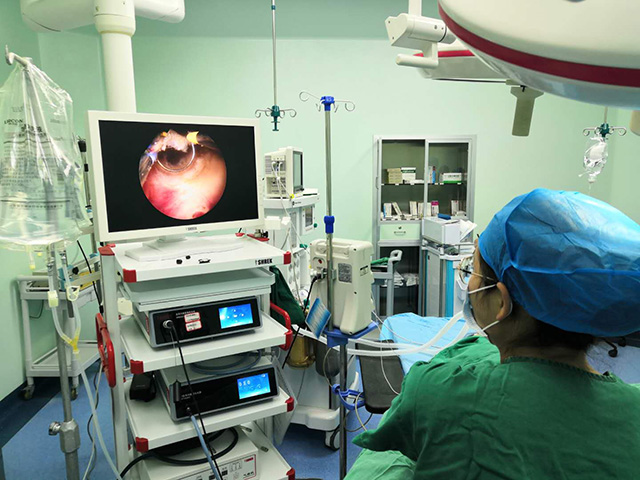
Insertion: The endoscope is then inserted through the mouth and down the throat. The endoscope is a long, flexible tube with a camera on the end. The camera captures images of the throat and displays them on a screen.
Examination: The doctor will move the endoscope around the throat to get a good view of the area. They may ask the patient to make certain sounds or swallow to observe the movement of the vocal cords and the muscles in the throat.
Removal: Once the examination is complete, the endoscope is gently removed from the patient's mouth.
The images captured by the endoscope can be used to diagnose various conditions of the throat, such as inflammation, infection, tumors, or other abnormalities. The procedure is usually safe and well-tolerated, but it may cause some discomfort or a gagging sensation.






Leave A Inquiry