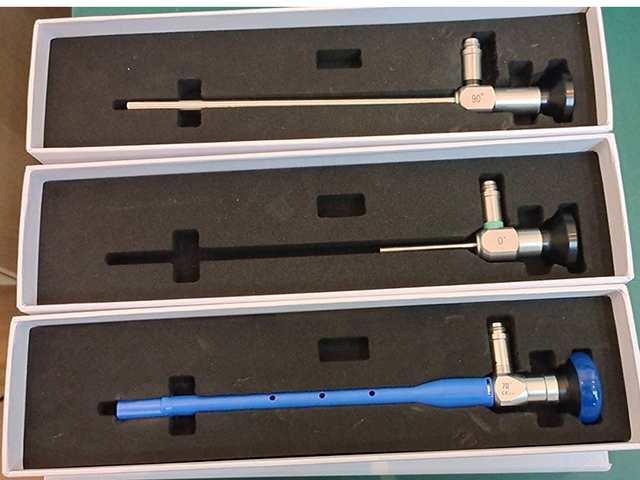
A urinary endoscope is a specialized instrument used to visualize the inside of the urinary tract, including the bladder, urethra, and kidneys. The composition of a urinary endoscope typically includes several components that work together to provide a clear and detailed view of the urinary system.
Here are the main components of a typical urinary endoscope:
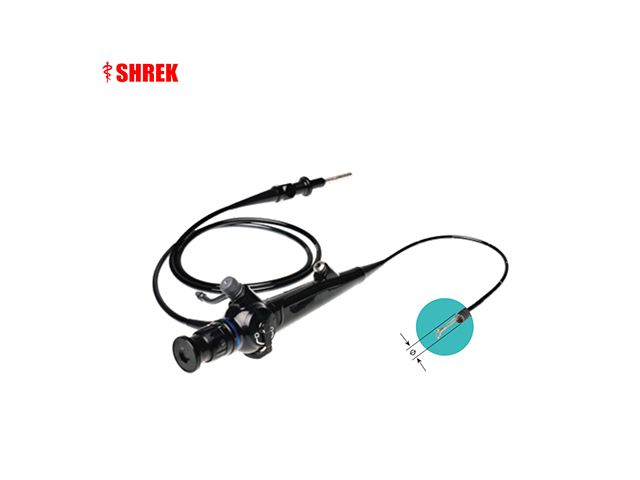
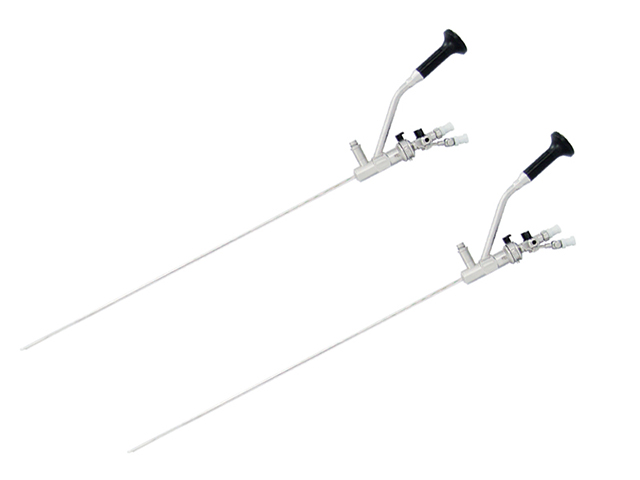
Insertion tube: This is a flexible or rigid tube that is inserted into the urethra and advanced into the bladder. The insertion tube typically has a diameter of a few millimeters and is composed of high-quality materials that are durable and resistant to damage.
Light source: A light source is typically located at the distal end of the insertion tube and provides illumination for the internal structures of the urinary tract. The light source is typically an LED or fiber optic bundle that delivers bright, high-quality light to the area being examined.
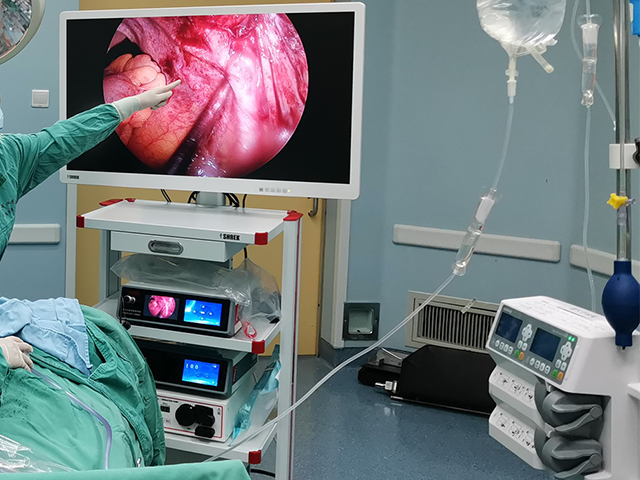
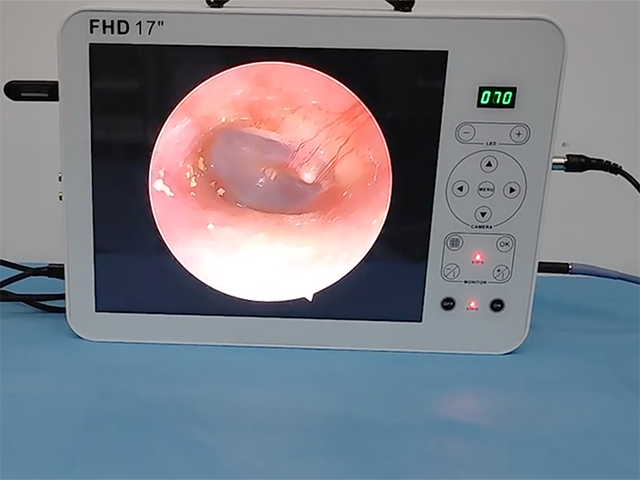
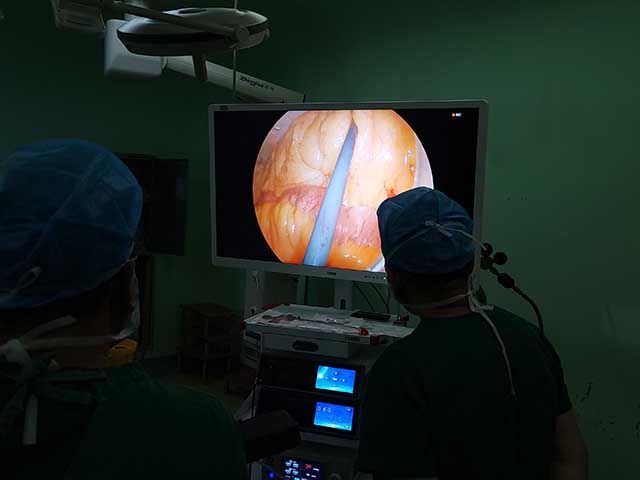
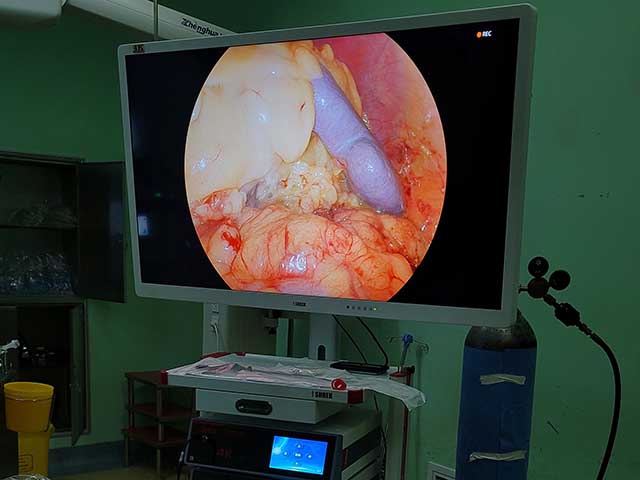
Camera: The camera is located at the distal end of the insertion tube and captures images of the internal structures of the urinary tract. The camera may be a high-resolution digital camera or a traditional analog camera, depending on the specific instrument.
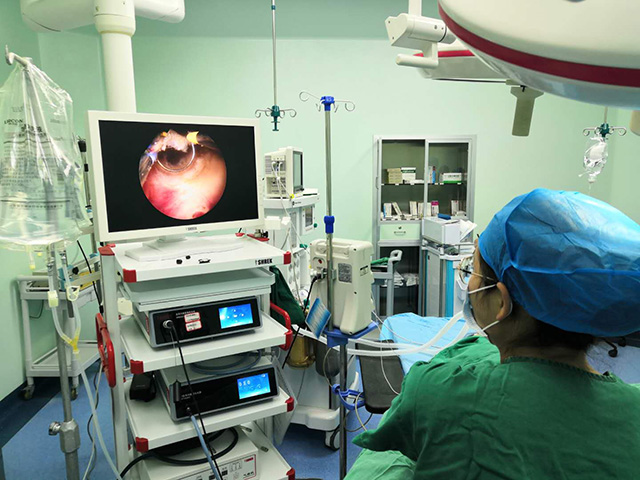
Control unit: The control unit is typically located outside the body and is used to control the movement of the insertion tube, adjust the light source, and capture and display images from the camera. The control unit may also include software for image processing and recording.
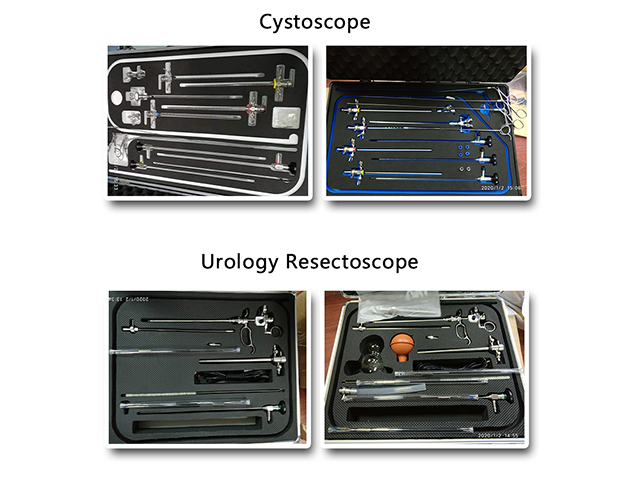
Accessories: Urinary endoscopes may also come with a range of accessories, such as biopsy forceps, irrigating sheaths, and suction devices, that are used to perform diagnostic or therapeutic procedures during the examination.
Overall, a urinary endoscope is a complex instrument that combines advanced optics, lighting, and imaging technology to provide doctors with a clear and detailed view of the urinary tract.






Leave A Inquiry