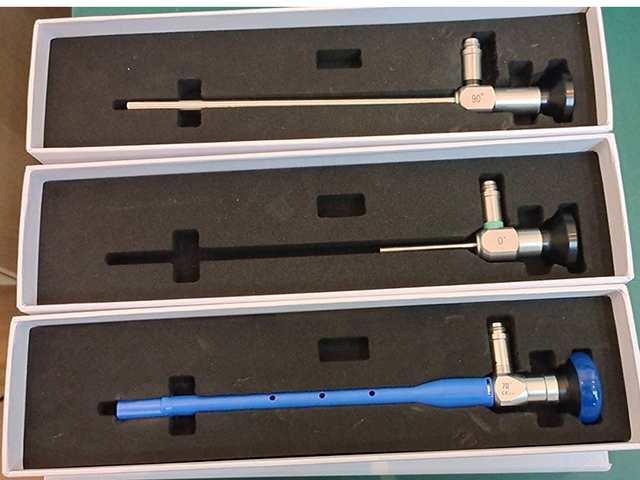
Endoscopy is a medical procedure that allows doctors to visualize the inside of the body using a specialized instrument called an endoscope. An endoscope is a flexible or rigid tube with a camera and light source attached to the end, which is inserted into the body through a natural opening, such as the mouth, nose, anus, or urethra, or through a small incision in the skin.
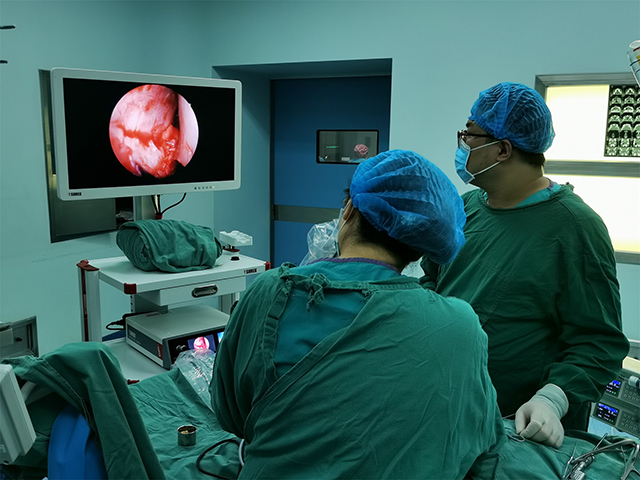
Endoscopy offers several advantages in clinical application, including:
Minimally invasive: Endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure, which means it requires smaller incisions or no incisions at all, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster recovery times compared to traditional surgical procedures.
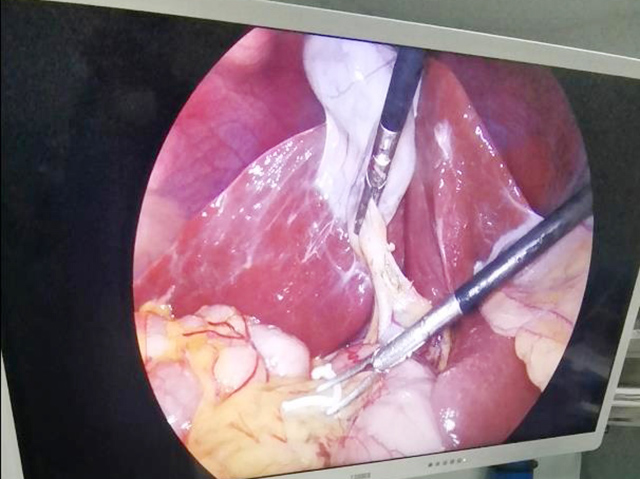
Visualization of internal structures: Endoscopy allows for direct visualization of internal structures, such as the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, urinary tract, and reproductive organs, providing valuable diagnostic and therapeutic information.
Precise diagnosis: Endoscopy enables precise diagnosis by allowing direct visualization of the affected area and obtaining tissue samples for biopsy.
Targeted treatment: Endoscopy allows for targeted treatment of specific conditions, such as removing polyps, treating bleeding or blockages, or performing minimally invasive surgeries.
Reduced hospital stay: Endoscopy procedures are often performed on an outpatient basis, reducing the need for hospitalization and promoting faster recovery times.
Improved patient outcomes: Endoscopy has been shown to improve patient outcomes and satisfaction by providing more accurate diagnoses and targeted treatments.
Safe and effective: Endoscopy is a safe and effective procedure when performed by a trained medical professional, with a low risk of complications and side effects.
Overall, endoscopy is a valuable tool in clinical practice, offering many advantages over traditional diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, with reduced risk and improved patient outcomes.


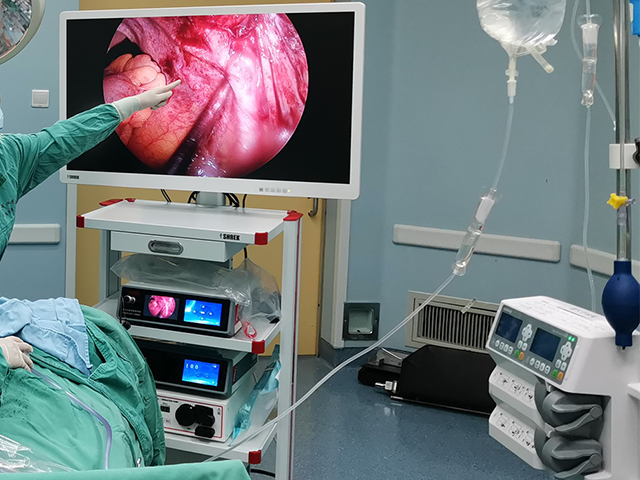

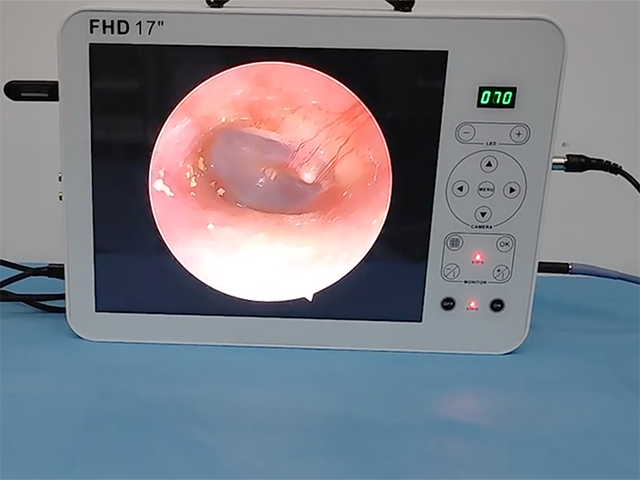
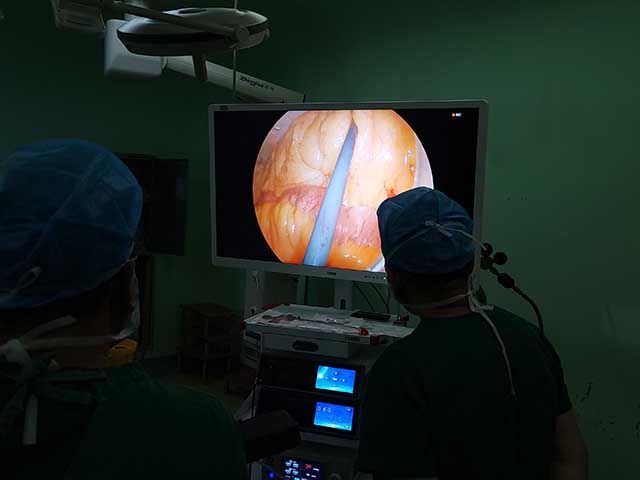



Leave A Inquiry