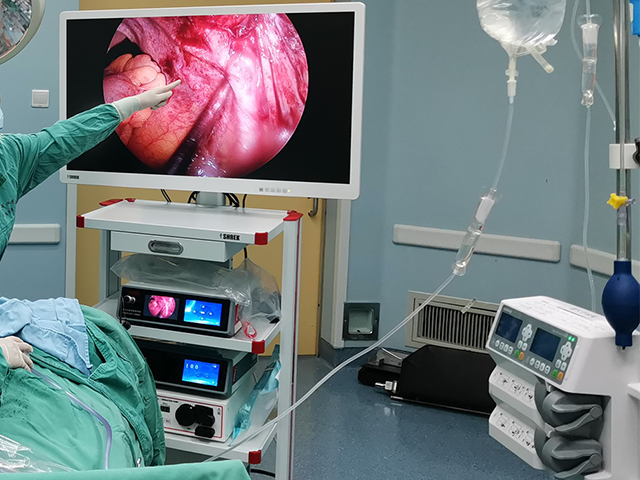
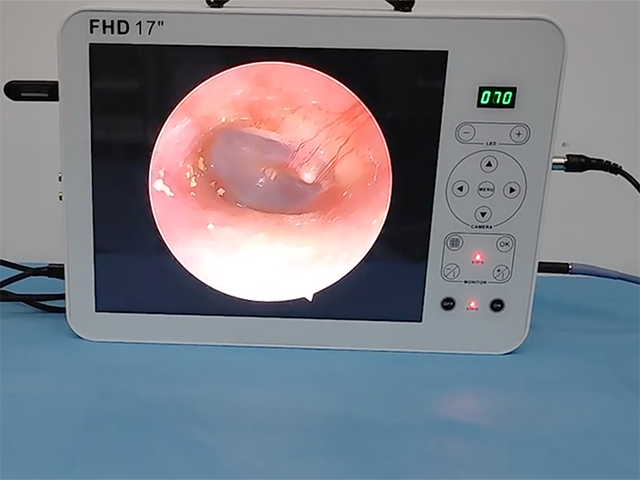
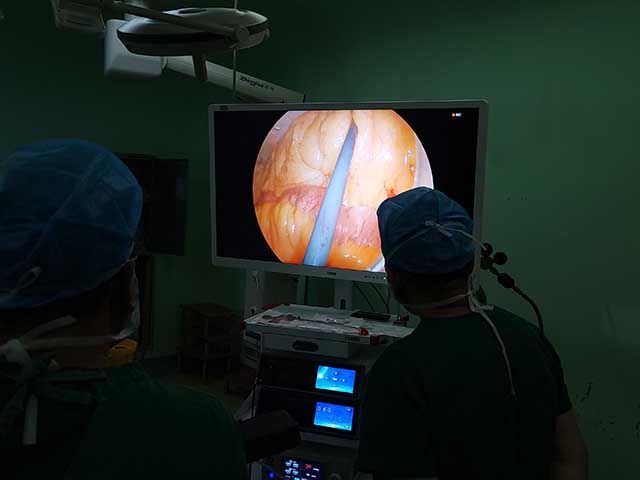
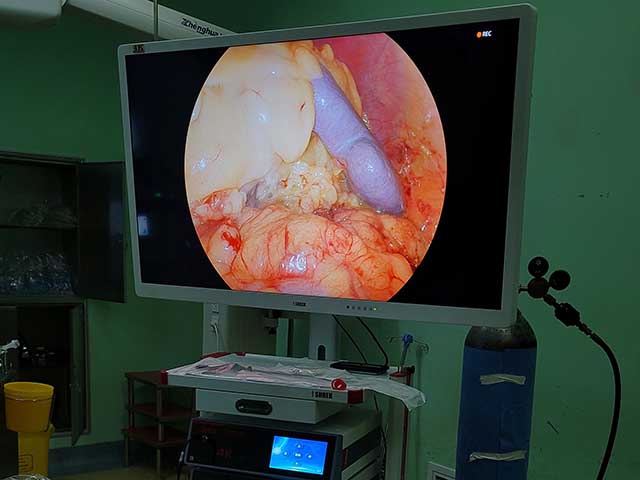
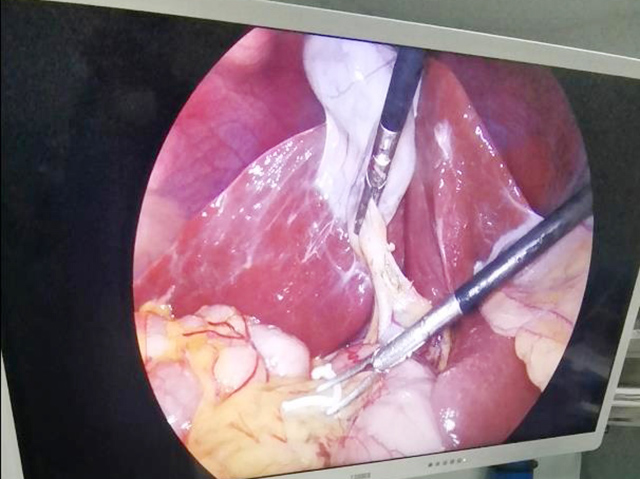
3D endoscopy, also known as stereoscopic endoscopy, uses two separate images captured by two cameras positioned a short distance apart to create the illusion of depth perception, similar to how our eyes see the world in three dimensions. The two images are then projected onto a monitor or other display device, which creates the 3D effect for the viewer.
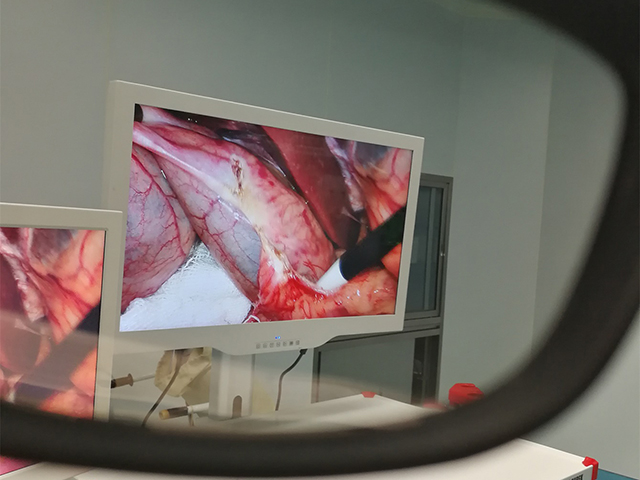
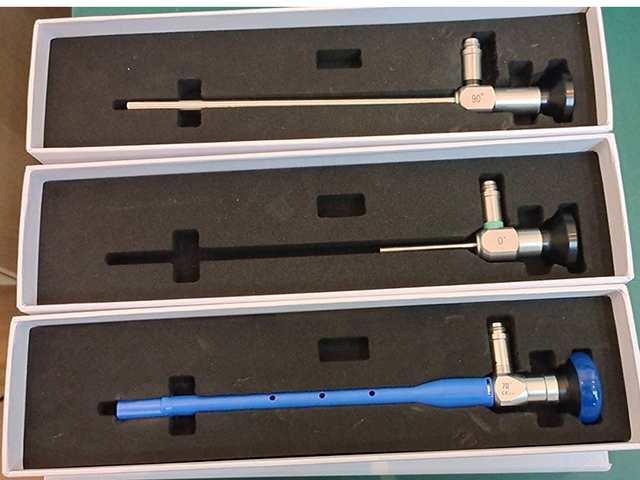
In a typical 3D endoscopy system, the two cameras are positioned at an angle to each other and are mounted on the end of the endoscope, which is inserted into the patient's body through a small incision or natural orifice. The cameras capture two slightly different views of the same object or tissue, which are then combined into a single 3D image by a computer algorithm.
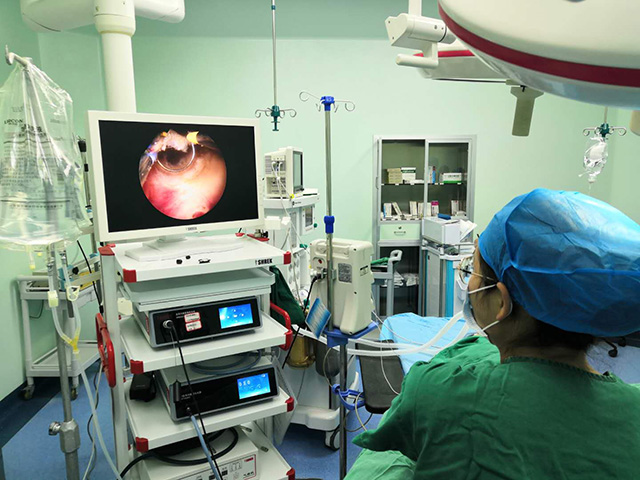
The 3D image is then displayed on a monitor or other display device that is equipped with special polarized or shuttered glasses that help create the illusion of depth perception. The viewer sees two separate images on the screen, one for each eye, which the brain then combines into a single 3D image.
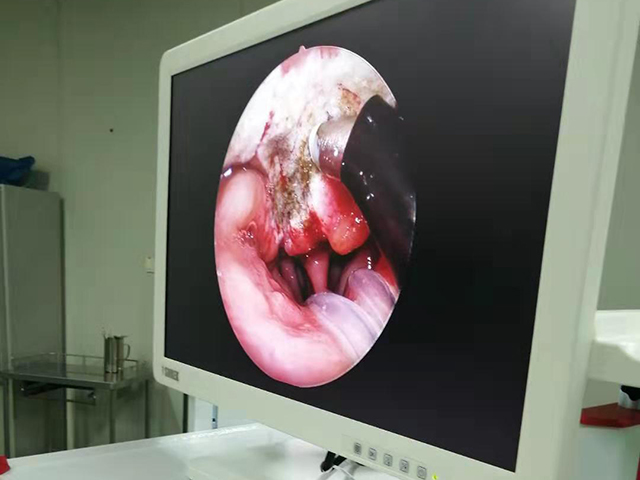
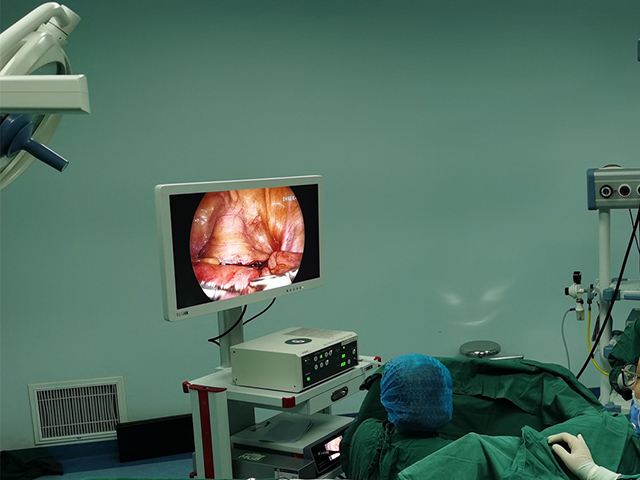
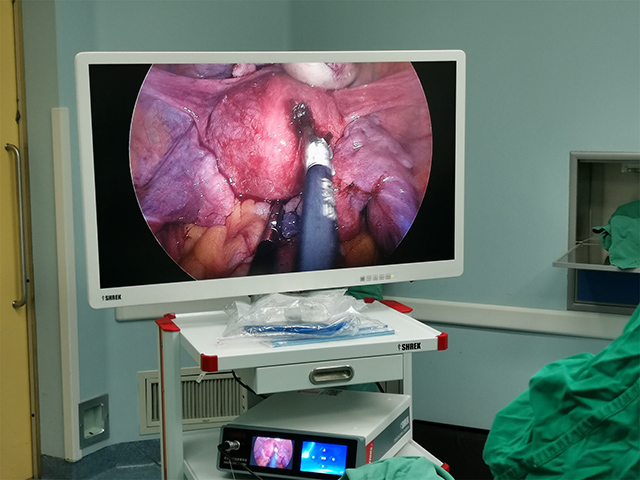
The benefits of 3D endoscopy include improved depth perception and spatial awareness, which can help surgeons perform procedures with greater accuracy and precision. It also allows for better visualization of complex anatomical structures, such as blood vessels and nerves, which can be difficult to see with traditional 2D endoscopy.
However, 3D endoscopy also has some limitations, including the need for specialized equipment and the potential for eye strain or fatigue for the viewer. Additionally, not all endoscopic procedures may benefit from 3D imaging, and the decision to use 3D imaging should be based on the specific needs of the patient and the procedure being performed.






Leave A Inquiry