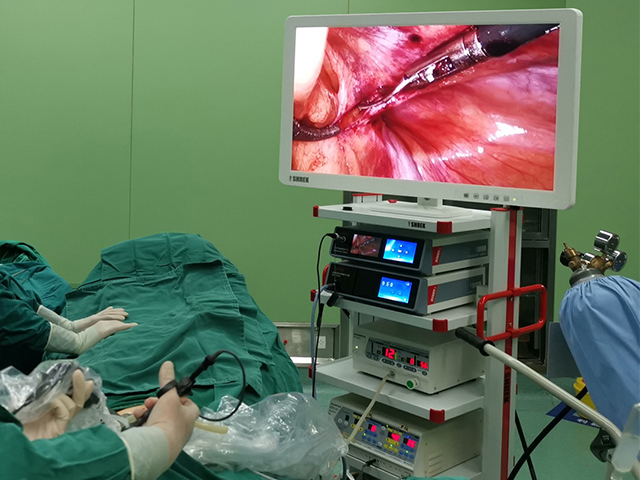
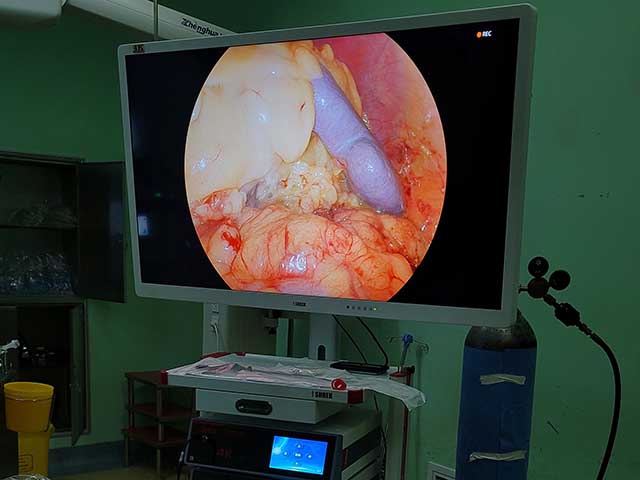
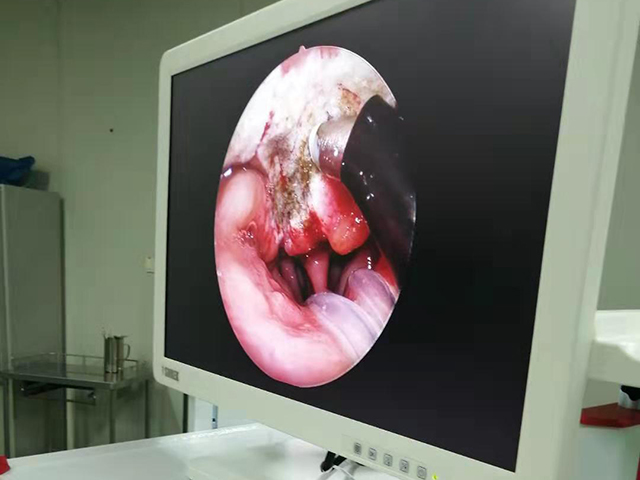
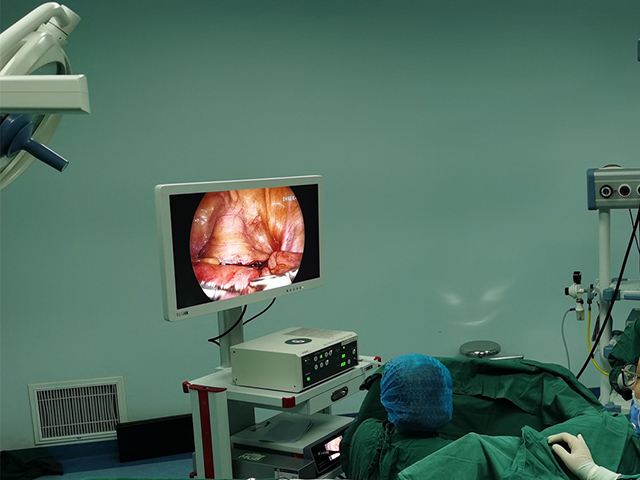
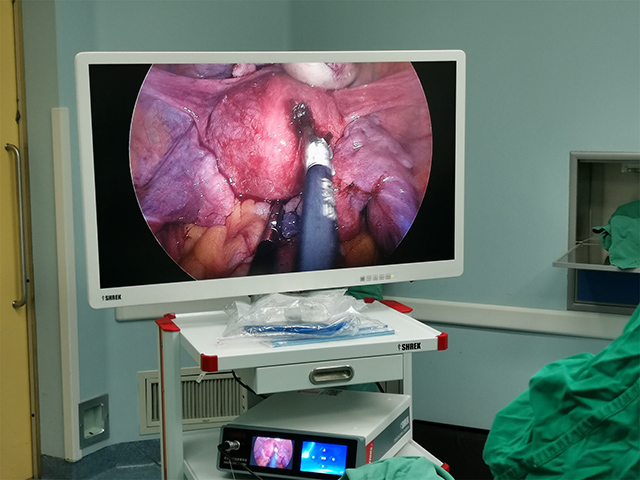
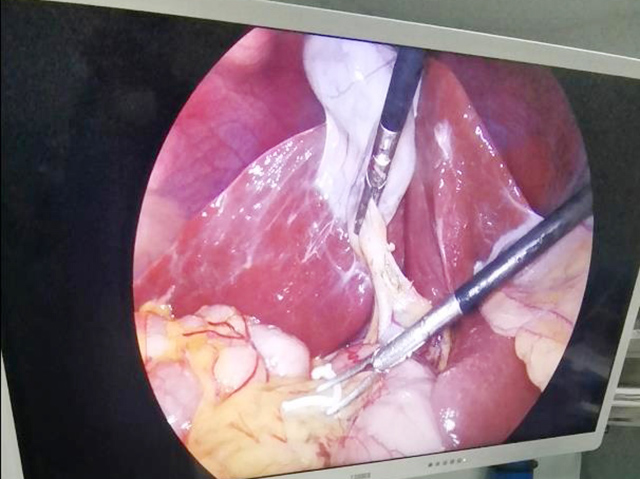
Medical endoscope camera systems are devices used in medical settings to provide visualization of internal body structures during diagnostic, therapeutic, and surgical procedures. An endoscope is a long, thin, flexible tube with a light source and a camera attached to its tip that is inserted into the body through a natural opening or a small incision.
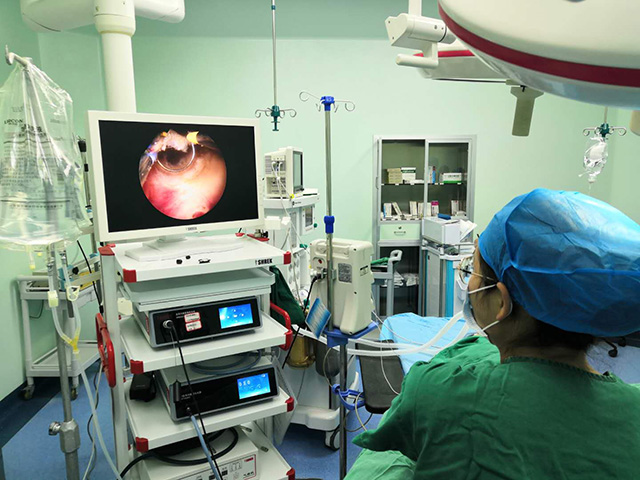
The camera system provides real-time video or still images of the internal structures, which can be viewed on a monitor or recorded for later review. Medical endoscope camera systems can be used for a wide range of procedures, including gastrointestinal examinations, respiratory evaluations, urological and gynecological exams, arthroscopic surgery, and neurosurgical procedures.
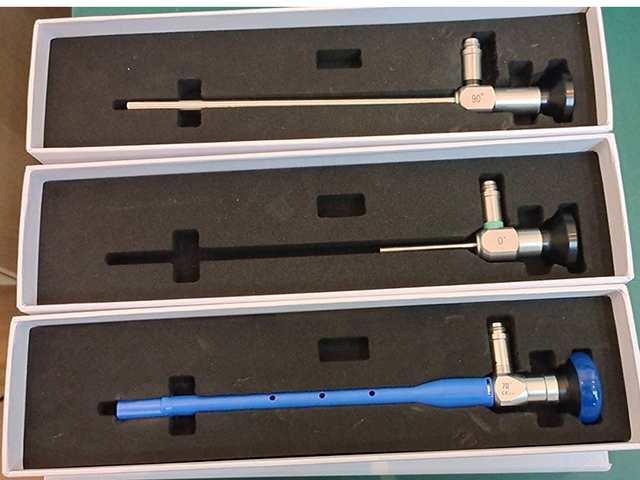
These camera systems consist of a high-resolution camera, a light source, and a control unit that allows the user to adjust the camera settings and control the light intensity. They are typically designed to be compatible with a variety of different types and sizes of endoscopes, and they may include additional features such as image enhancement, digital zoom, and data storage capabilities.
The technical requirements for medical endoscope camera systems may vary depending on the specific application and type of endoscope being used, but some general requirements may include:
Image quality: The camera system must be able to produce high-quality images with sufficient resolution, color fidelity, and contrast for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Light source: The camera system must have a compatible light source that can provide sufficient illumination for the endoscope's optics to capture clear images.
Connectivity: The camera system must be compatible with the hospital or clinic's existing equipment and interfaces, such as video displays, recording devices, and medical software.
Durability: The camera system must be rugged enough to withstand the rigors of clinical use and be designed to minimize the risk of infection transmission between patients.
Sterilization: The camera system must be capable of being thoroughly sterilized to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Ergonomics: The camera system must be designed to be comfortable and easy to use by clinicians, with intuitive controls and ergonomic design features.
Compatibility: The camera system must be compatible with the specific type of endoscope being used, including the size, shape, and type of optics and other components.
Adaptability: The camera system should be flexible enough to adapt to different clinical scenarios, such as endoscopic surgery, diagnostic procedures, and therapeutic interventions.
Recording: The camera system should be capable of recording high-quality video and images for documentation purposes and patient follow-up.
Overall, the technical requirements for medical endoscope camera systems are aimed at ensuring high-quality, safe, and effective clinical outcomes for patients.






Leave A Inquiry