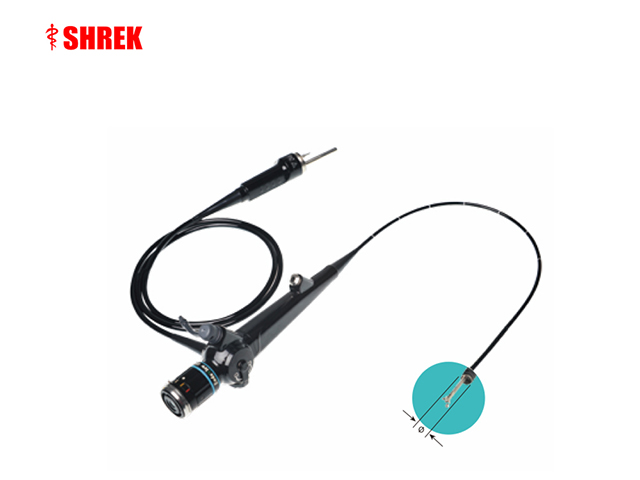

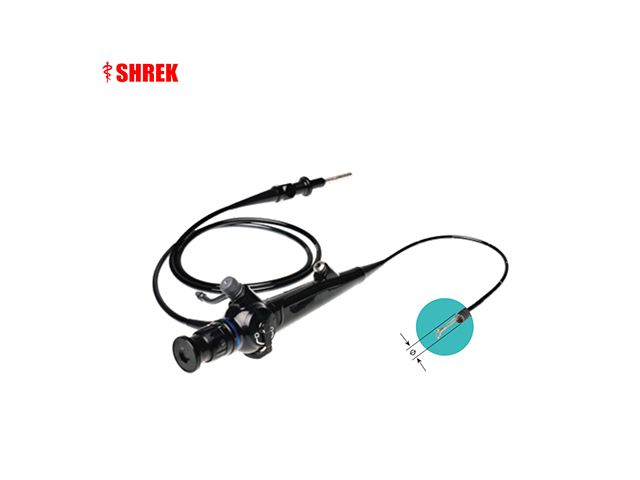
Fiberoptic endoscopy is a technique used to visualize the inside of the body using a thin, flexible, fiber-optic instrument known as an endoscope. Gastroscopy is a type of endoscopy that specifically examines the inside of the upper gastrointestinal tract, including the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
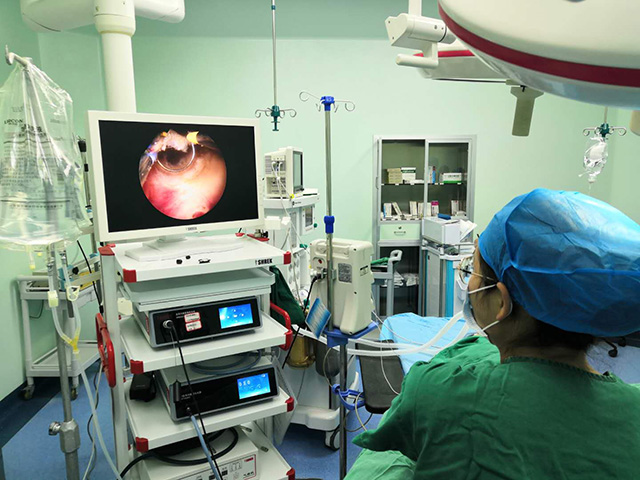
Gastroscopy can be performed using a fiberoptic endoscope, which allows for high-resolution visualization of the digestive tract using fiber-optic technology. The fiberoptic endoscope has a light source and a camera at the tip, which transmits images of the digestive tract to a monitor for viewing.
Other types of endoscopy may use different instruments, such as a video endoscope, which uses digital technology to capture and transmit images of the digestive tract to a monitor. However, regardless of the specific instrument used, endoscopy involves the insertion of a flexible tube through the mouth, down the throat, and into the digestive tract to visualize the internal structures and diagnose or treat any abnormalities.






Leave A Inquiry