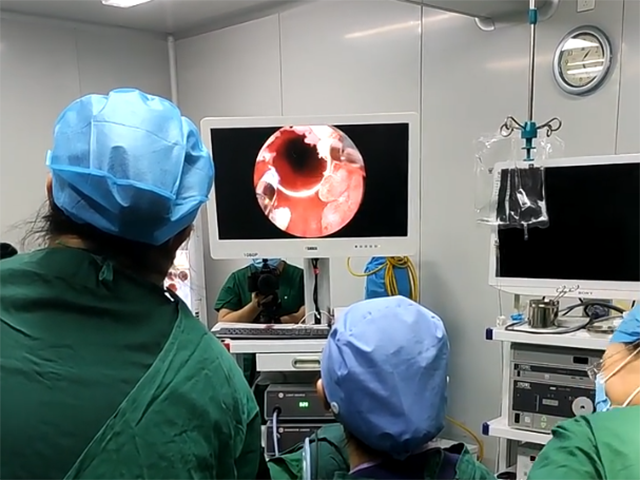
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves the insertion of a narrow tube with a camera into the uterus to diagnose and treat various uterine conditions, including intrauterine adhesions. Intrauterine adhesions, also known as Asherman's syndrome, occur when scar tissue forms within the uterus, often as a result of trauma, such as a previous uterine surgery or infection. Hysteroscopy can be a valuable tool in diagnosing and treating this condition.
Diagnosis of Intrauterine Adhesions:
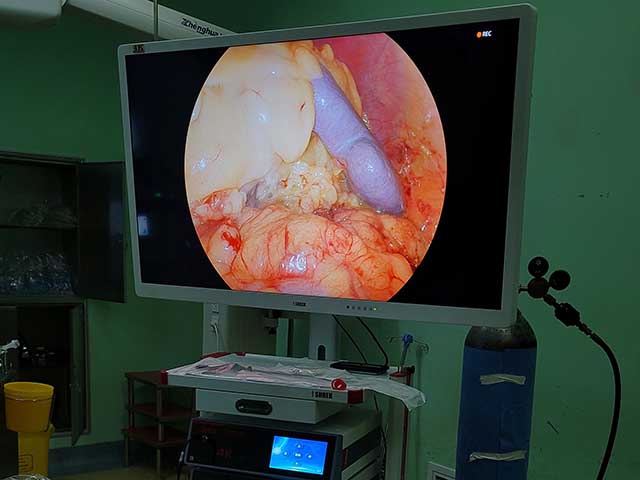
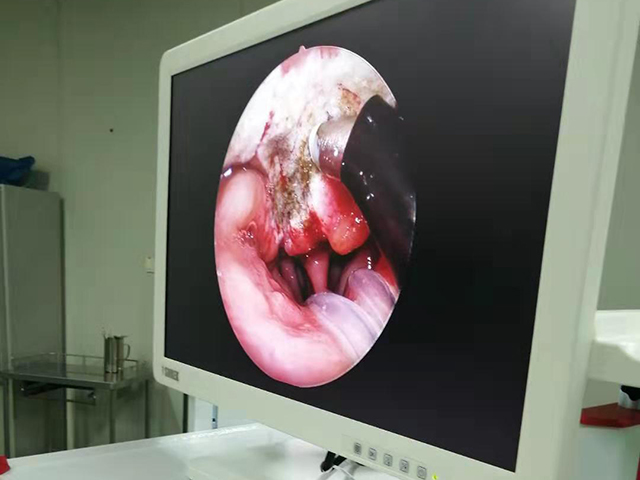
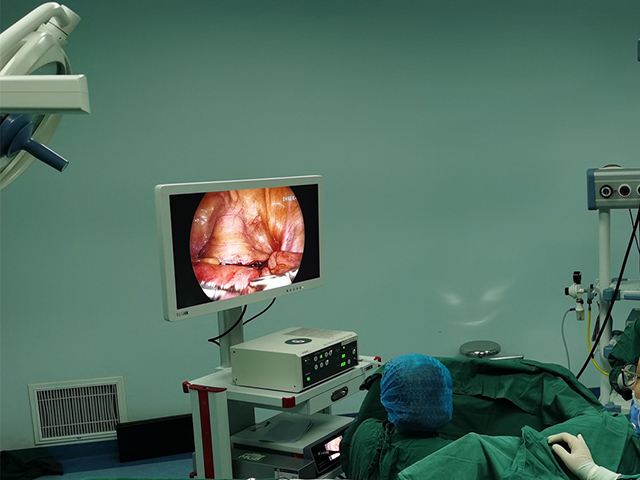
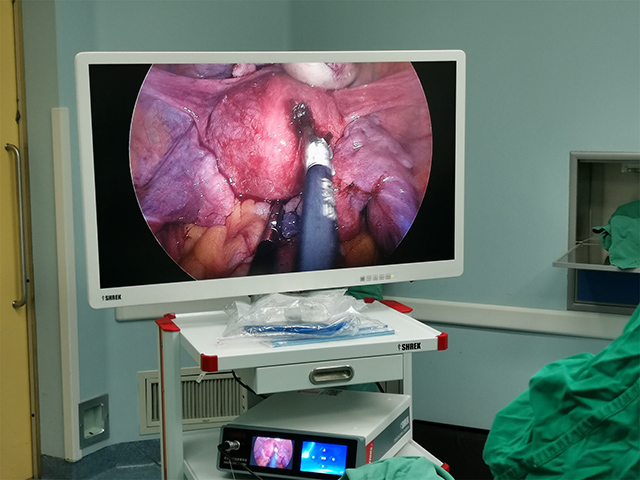
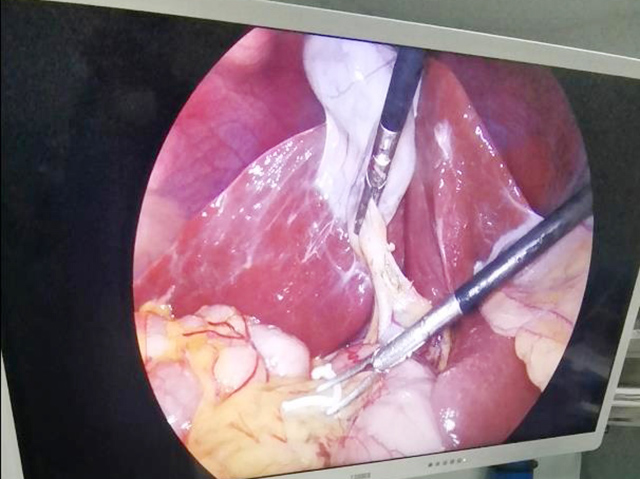
Hysteroscopy allows direct visualization of the uterine cavity, enabling the physician to identify any abnormal tissue, including intrauterine adhesions. During hysteroscopy, a small camera is inserted into the uterus, providing real-time images of the uterine cavity. The physician can identify the location and extent of the adhesions and evaluate the overall health of the uterine lining.
Treatment of Intrauterine Adhesions:
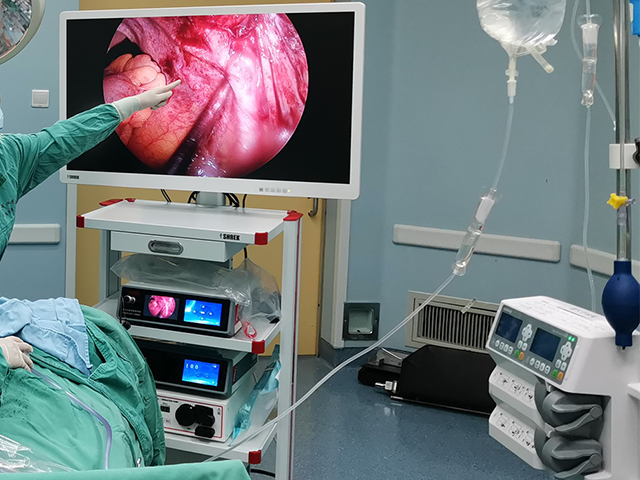
In addition to diagnosis, hysteroscopy can also be used to treat intrauterine adhesions. The physician can use various tools, such as scissors or lasers, to remove the adhesions and restore the normal anatomy of the uterus. The procedure is minimally invasive and does not require any incisions, resulting in a shorter recovery time.
Post-Treatment Follow-up:
Following the removal of intrauterine adhesions, it is essential to monitor the healing process and ensure that the adhesions do not reform. Hysteroscopy can be used for follow-up exams to evaluate the success of the treatment and identify any recurrence of adhesions.
In summary, hysteroscopy is a valuable tool in the diagnosis and treatment of intrauterine adhesions. It provides a minimally invasive approach to visualize the uterine cavity and remove adhesions, resulting in a faster recovery time and a higher success rate.






Leave A Inquiry