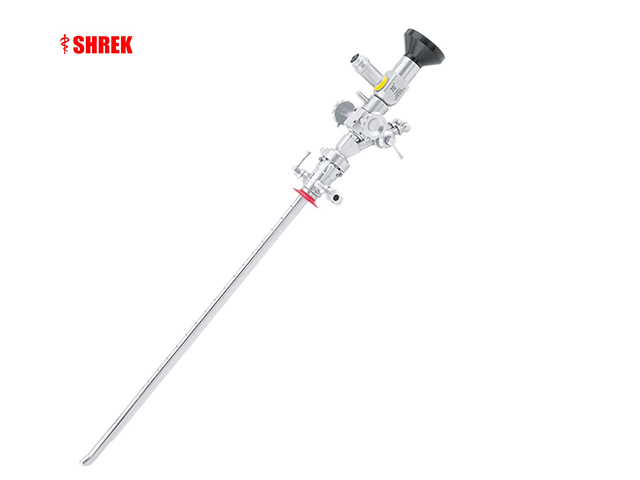

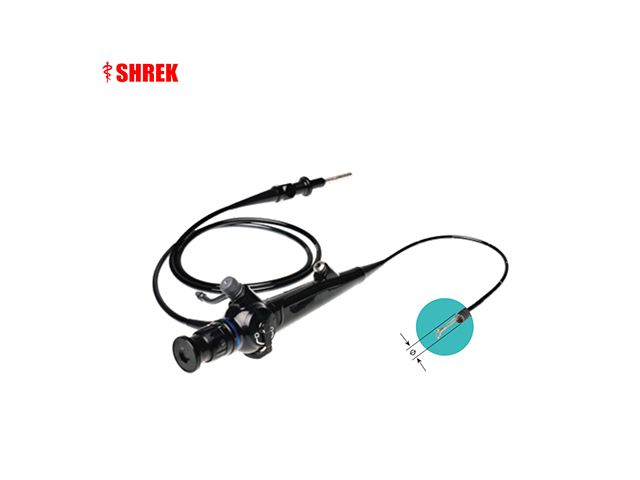
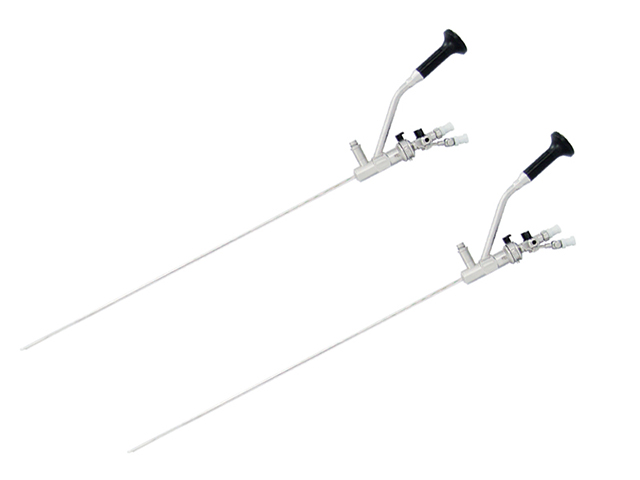
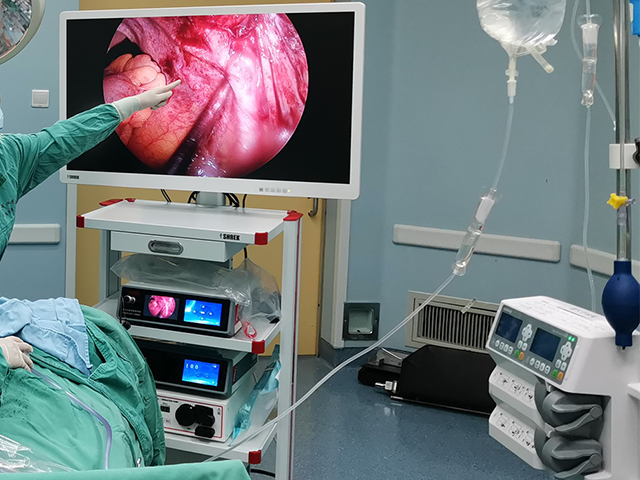
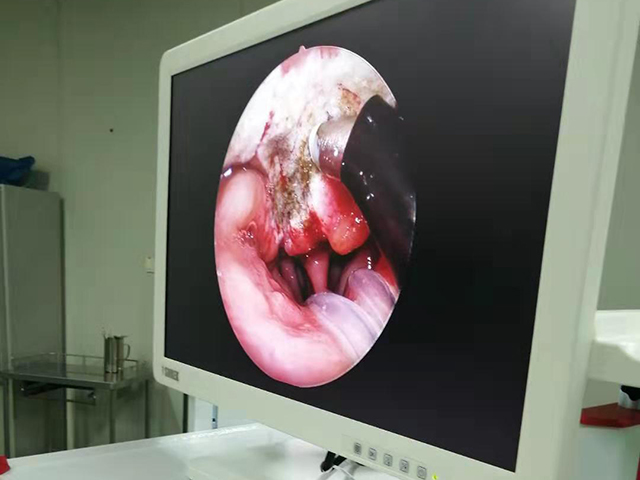
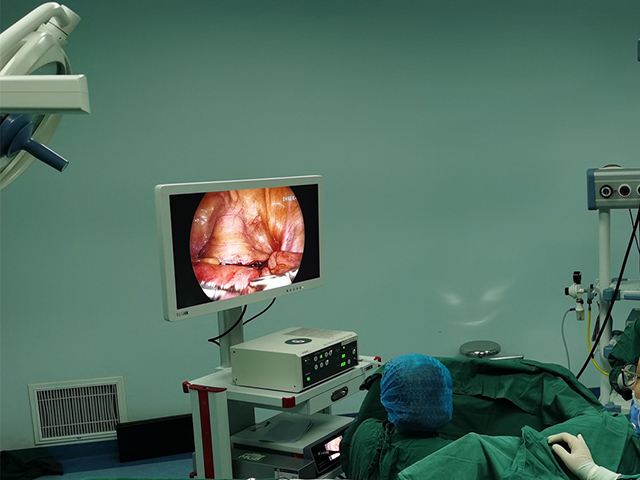
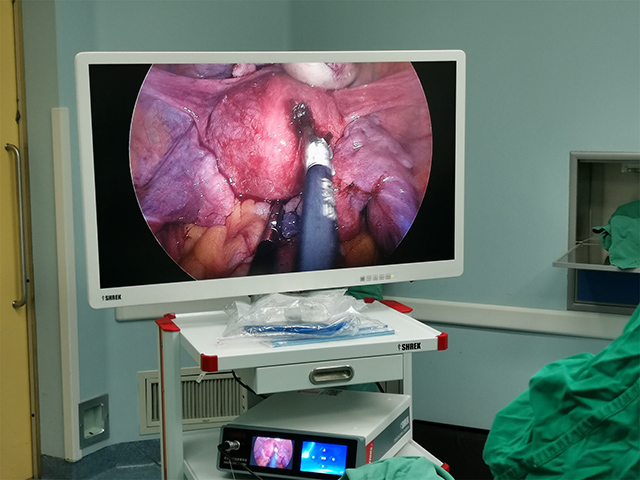
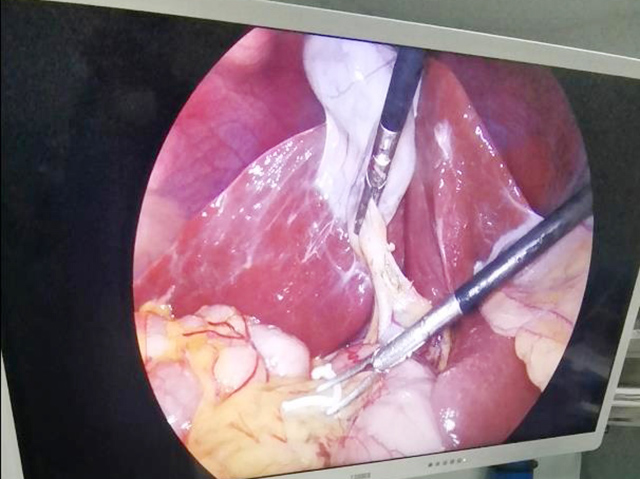
A cystoscope is a type of urologic endoscope that is used to examine the bladder and urethra. The device consists of a thin, flexible or rigid tube with a light source and camera that allows the physician to view the inside of the bladder and urethra on a monitor. Here are some of the main features and uses of a cystoscope:
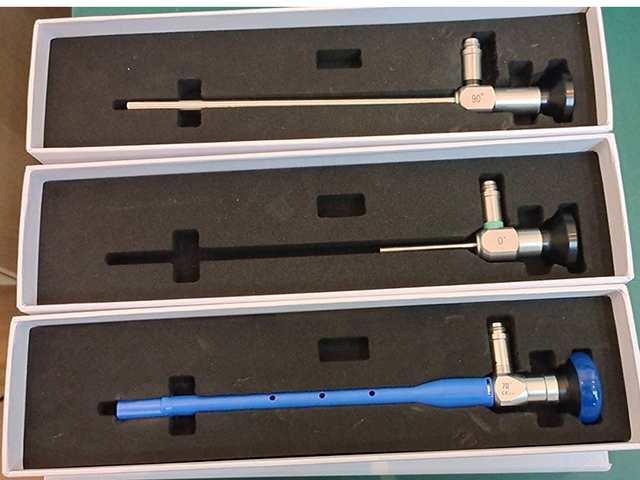
Size: Cystoscopes come in different sizes, ranging from 2.7mm to 9mm in diameter. The size of the scope is chosen based on the size of the patient's bladder and urethra.
Angle of view: The cystoscope can be straight or angled, depending on the area of the bladder or urethra being examined.
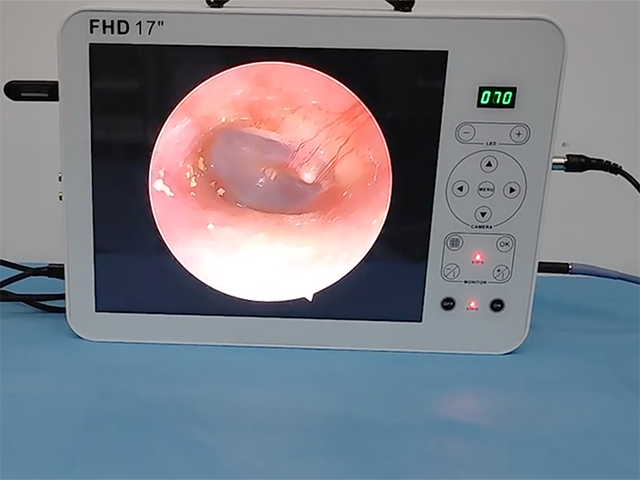
Light source: A light source is built into the cystoscope or is provided by an external source. The light illuminates the bladder and urethra, making it easier for the physician to see and examine the area.
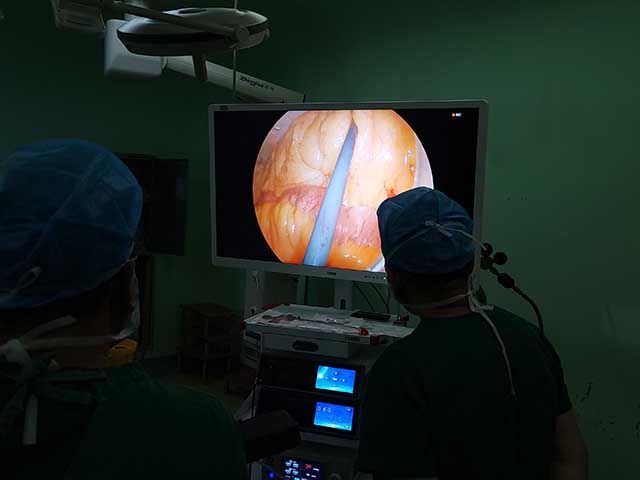
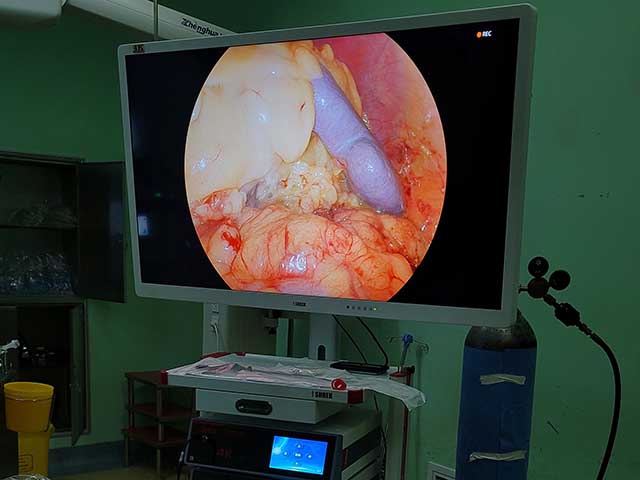
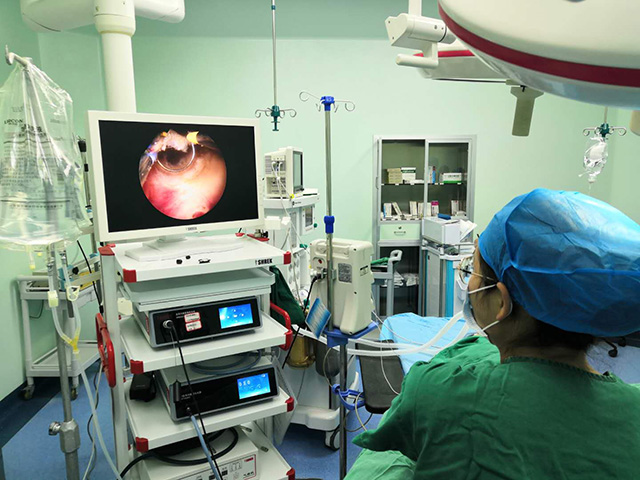
Camera: A camera is attached to the end of the cystoscope and provides a visual image of the bladder and urethra on a monitor.
Working channel: Some cystoscopes have a working channel that allows the physician to pass instruments through the scope to perform procedures or take tissue samples.
Cystoscopes are used for a variety of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, including:
Evaluation of urinary tract infections
Identification of bladder tumors or stones
Diagnosis of bladder cancer
Treatment of bladder cancer, such as transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT)
Placement of ureteral stents
Biopsy of bladder tissue
Advancements in technology have led to the development of newer cystoscope systems that offer high-definition images, improved maneuverability, and enhanced visualization. These features can provide better accuracy and precision during procedures and improve patient outcomes.






Leave A Inquiry