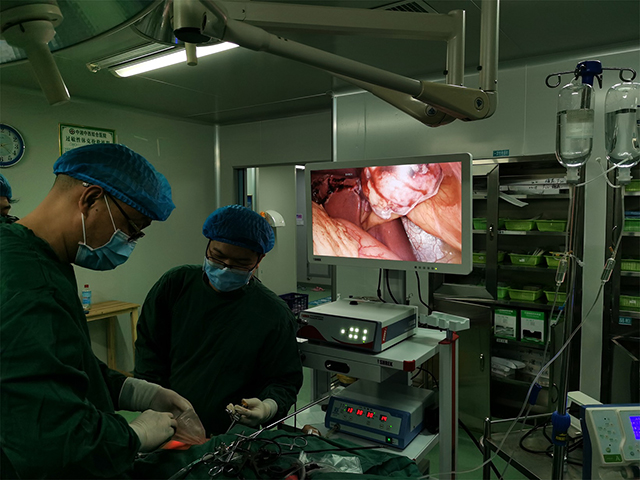
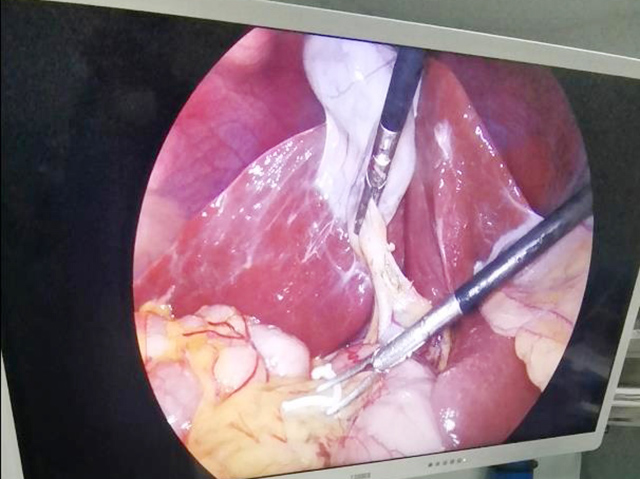
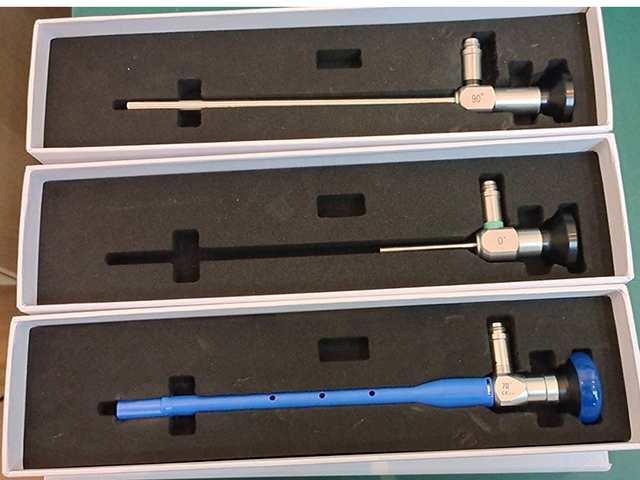
Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source attached (an endoscope) to examine and treat medical conditions within the abdomen or pelvis. The purpose of laparoscopy is to provide a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery, which requires a large incision and longer recovery time.
Laparoscopy can be used for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Diagnostic laparoscopy may be recommended if a patient has unexplained abdominal pain or other symptoms, or if other diagnostic tests have been inconclusive. During a diagnostic laparoscopy, the surgeon can visually inspect the abdominal organs, take tissue samples for biopsy, and look for signs of disease or other abnormalities.
Therapeutic laparoscopy is used to treat a variety of medical conditions within the abdomen or pelvis, including:
Removal of the gallbladder or appendix
Treatment of endometriosis or ovarian cysts
Repair of hernias or other abdominal wall defects
Removal of tumors or other abnormal tissue
Treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Treatment of obesity (bariatric surgery)
Overall, the purpose of laparoscopy is to provide a safe and effective alternative to traditional open surgery, with reduced pain, scarring, and recovery time. The specific type of laparoscopic procedure recommended will depend on the patient's individual needs and medical history.






Leave A Inquiry